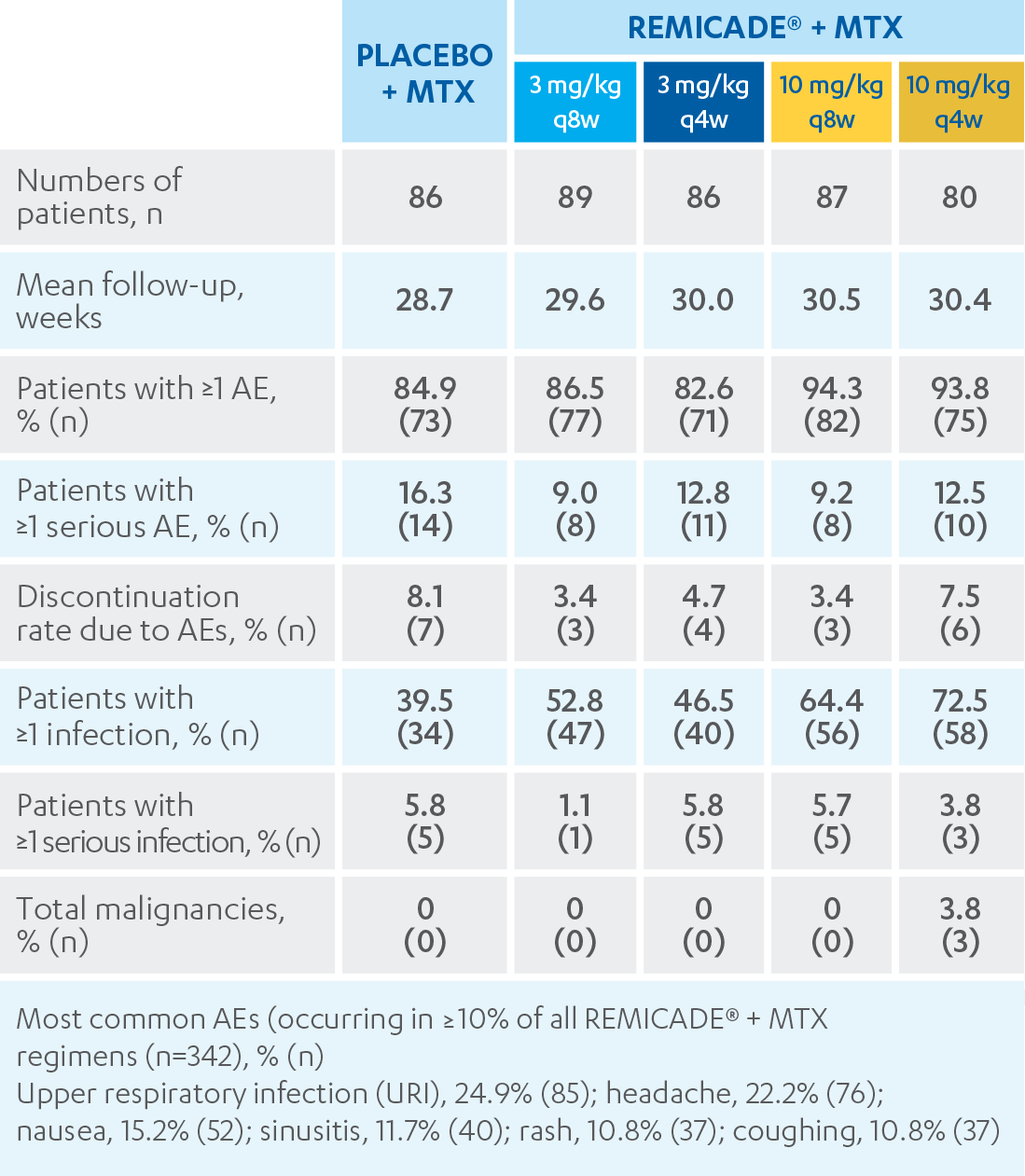
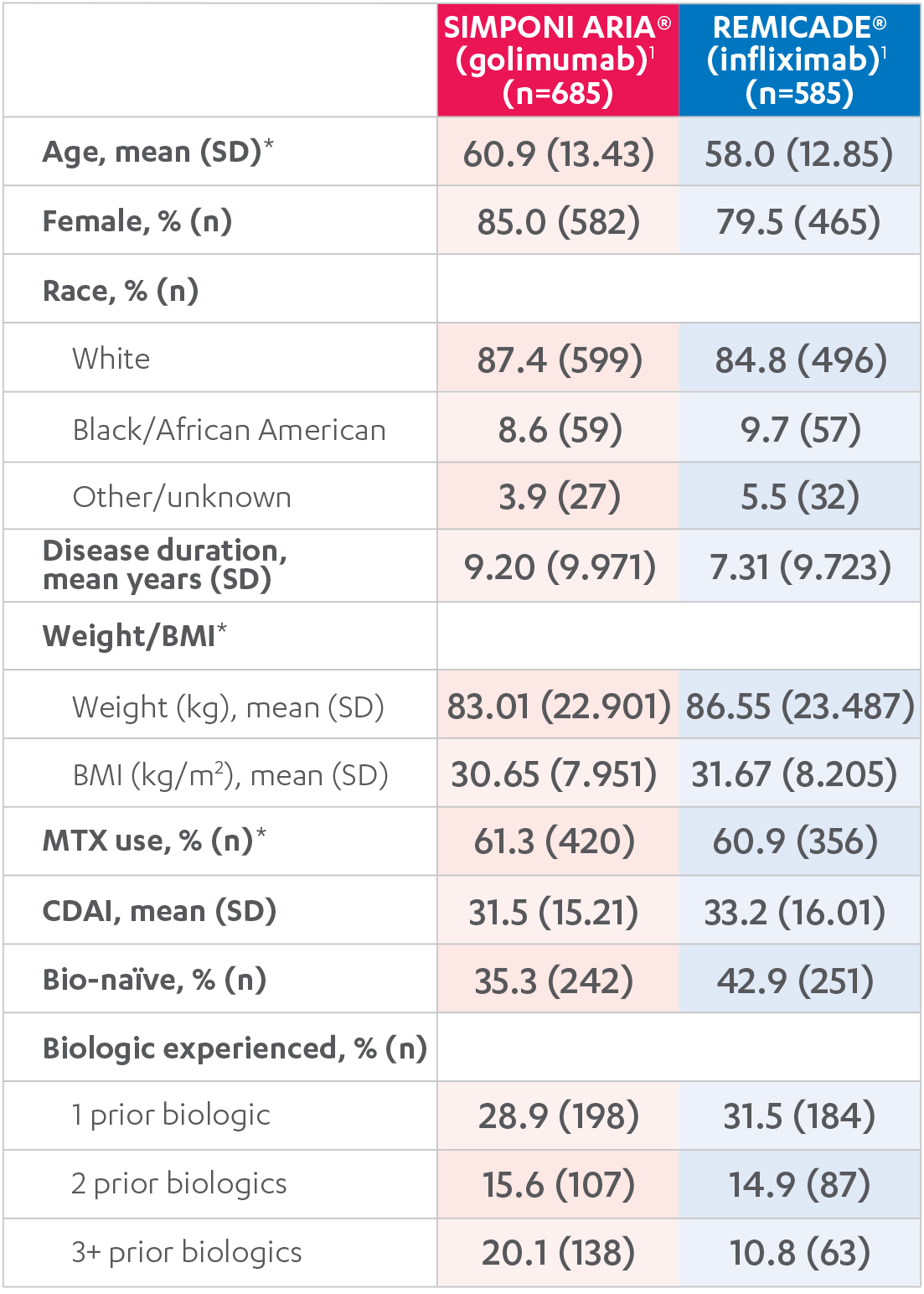
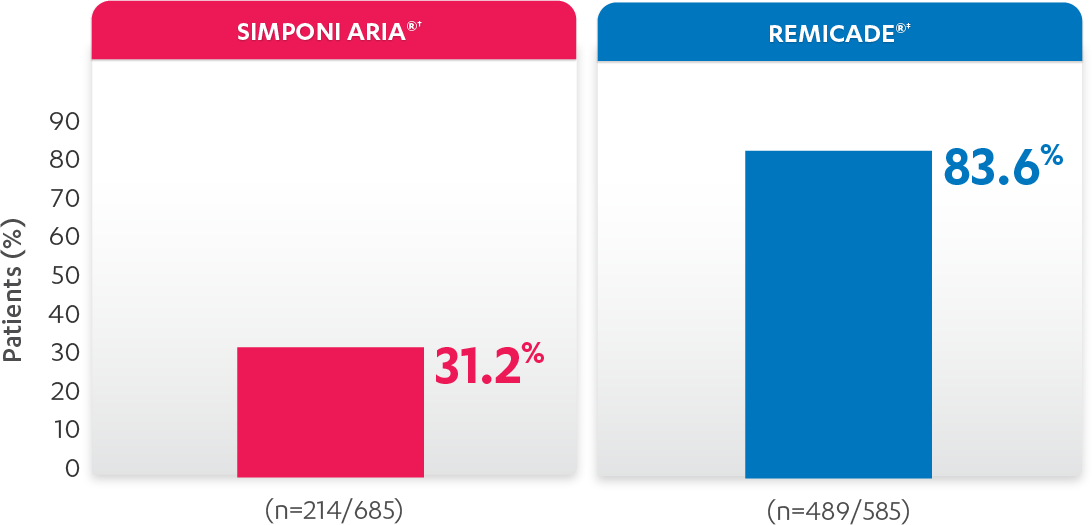
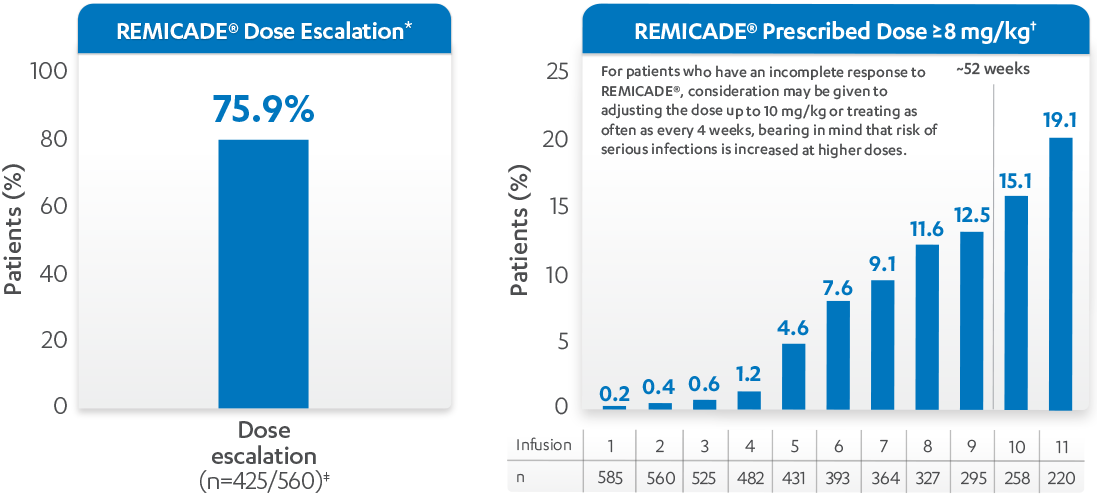
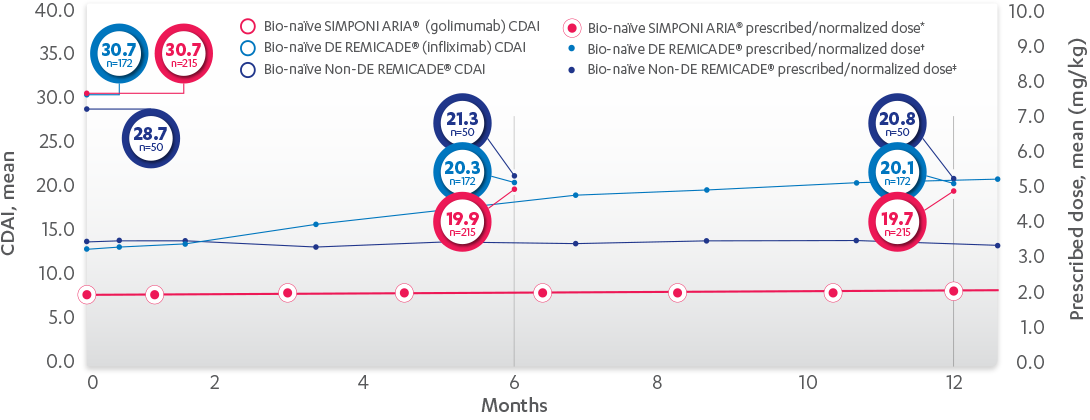
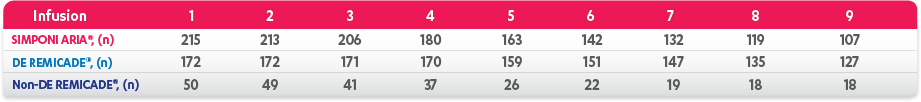
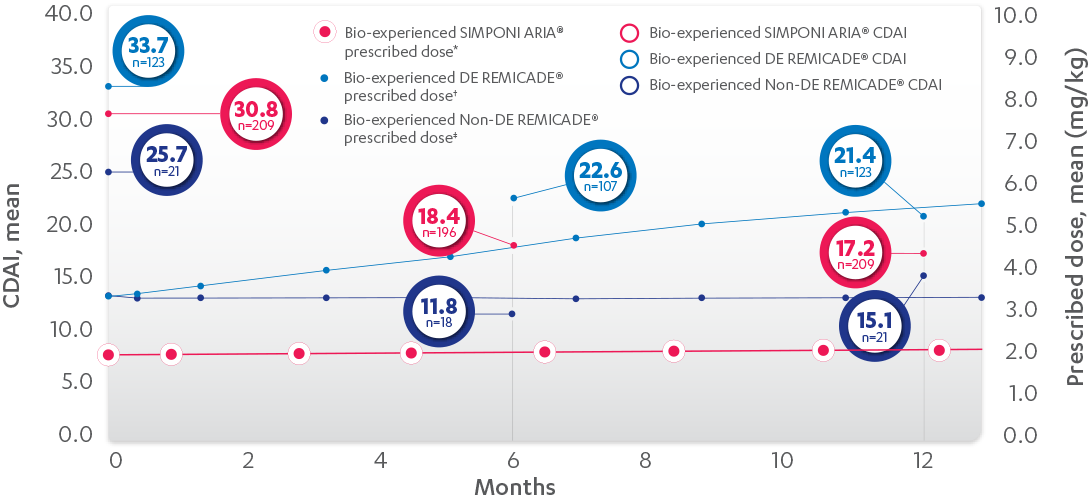
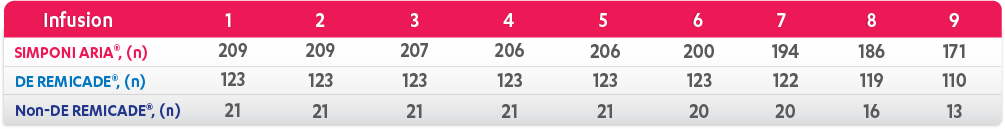
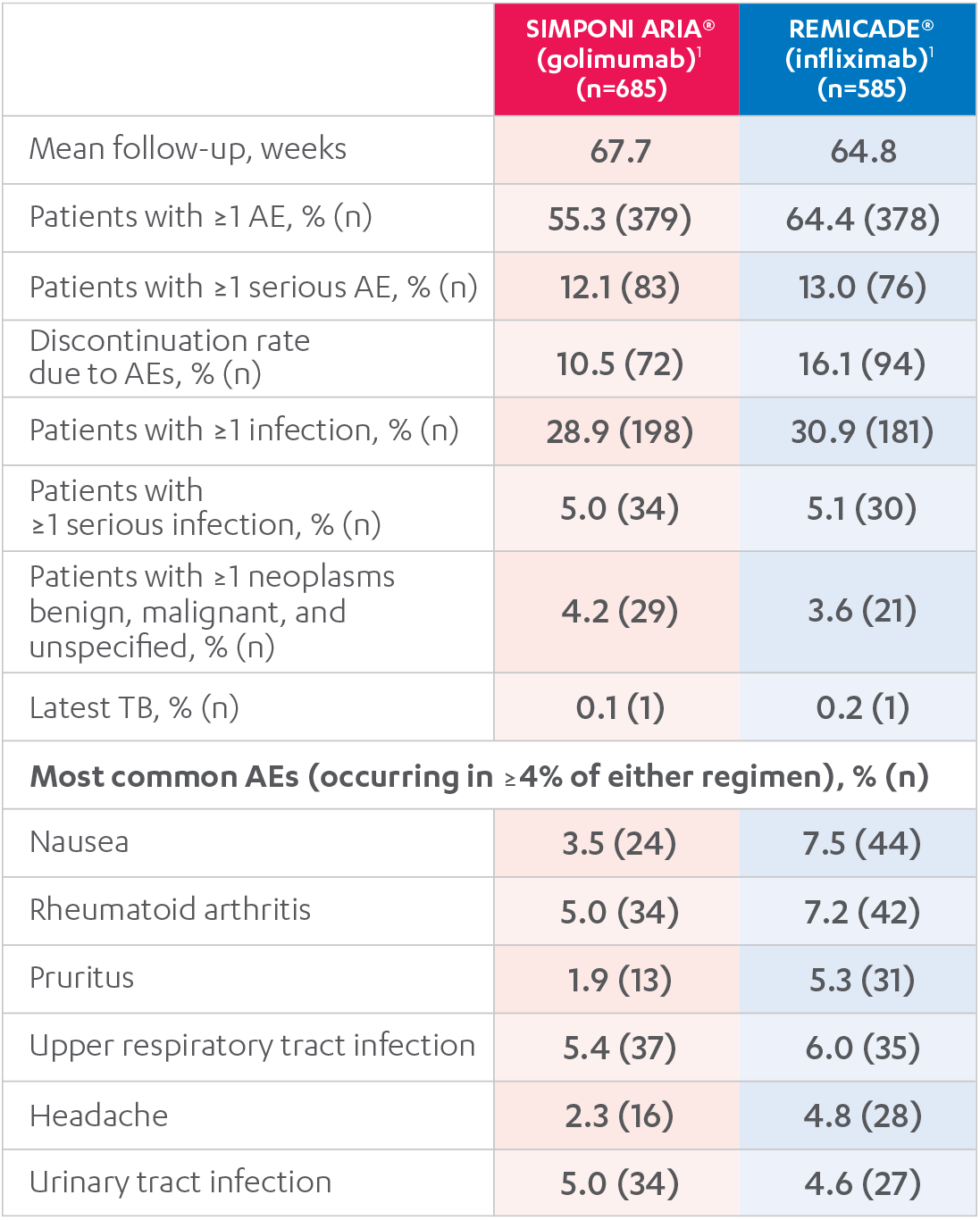
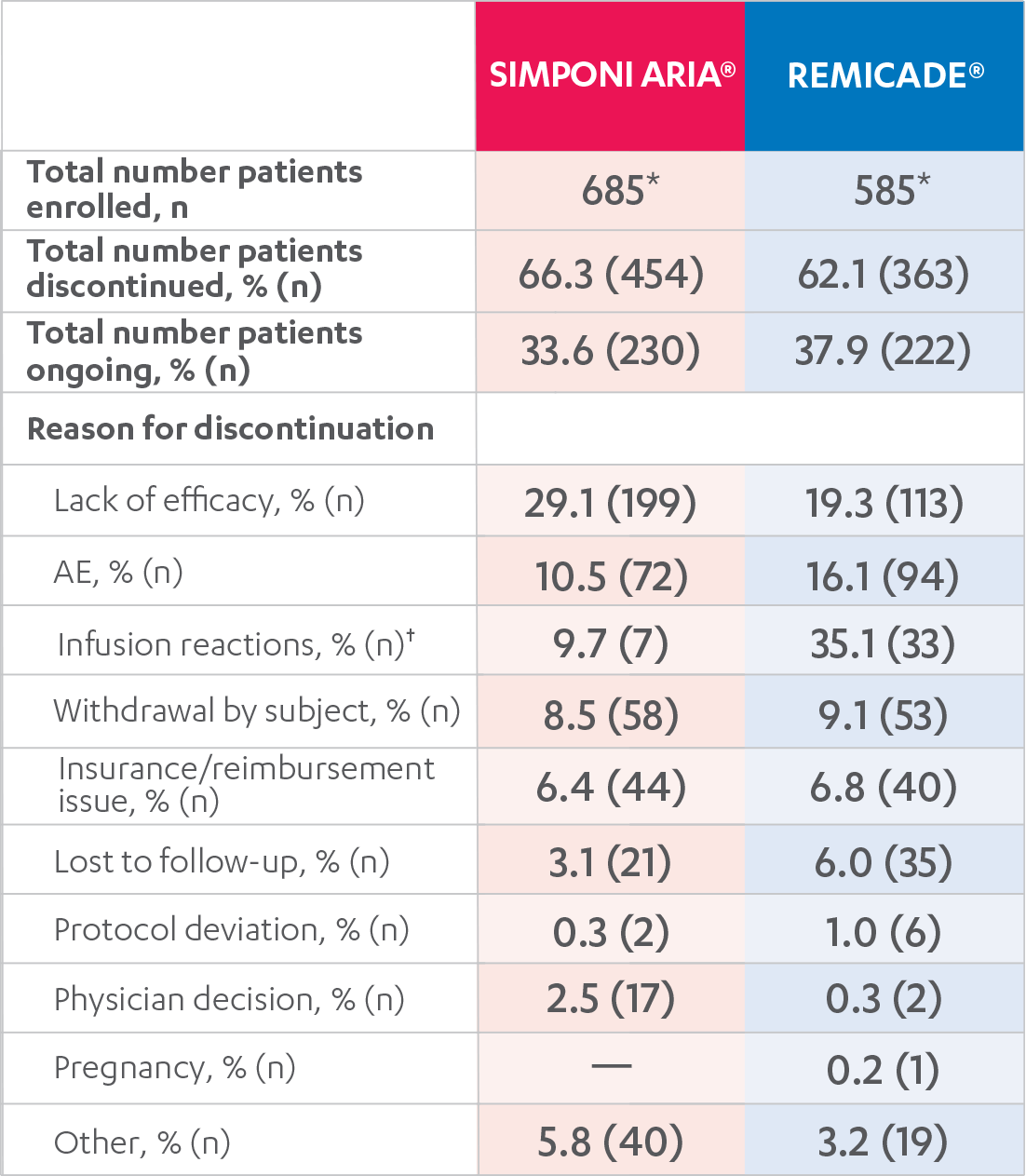
REMICADE® (infliximab) ATTRACT
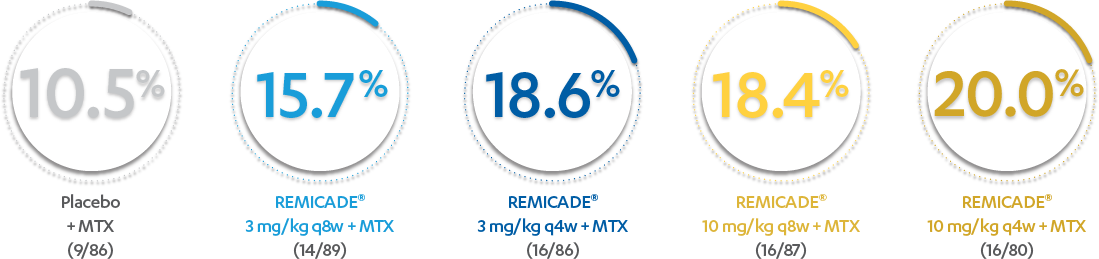
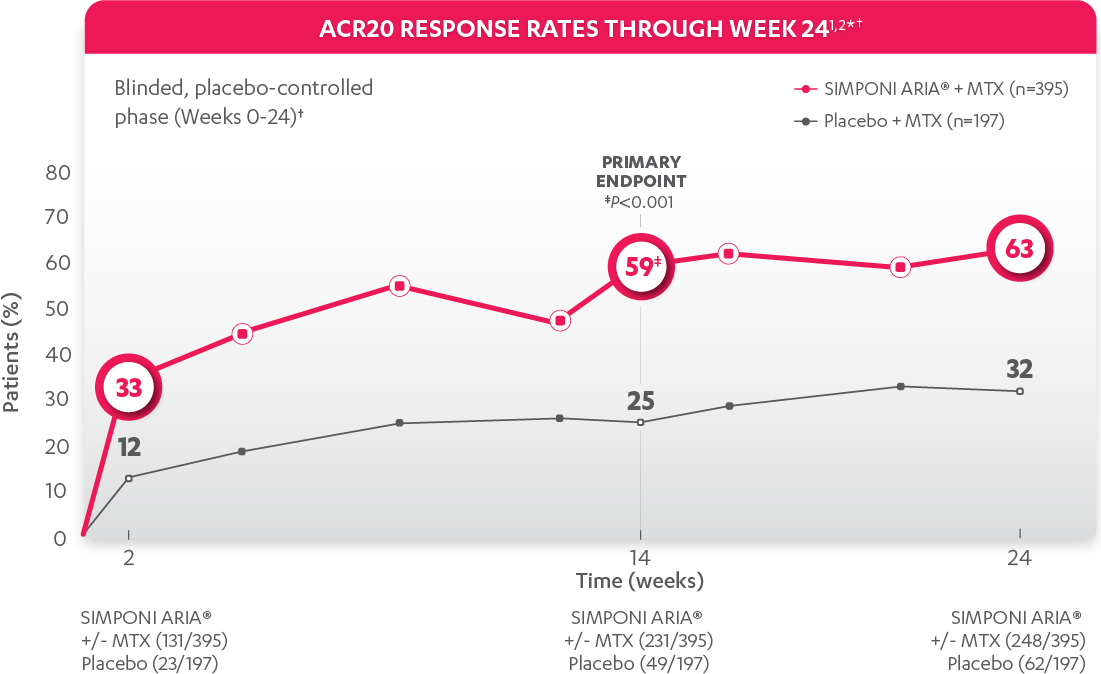
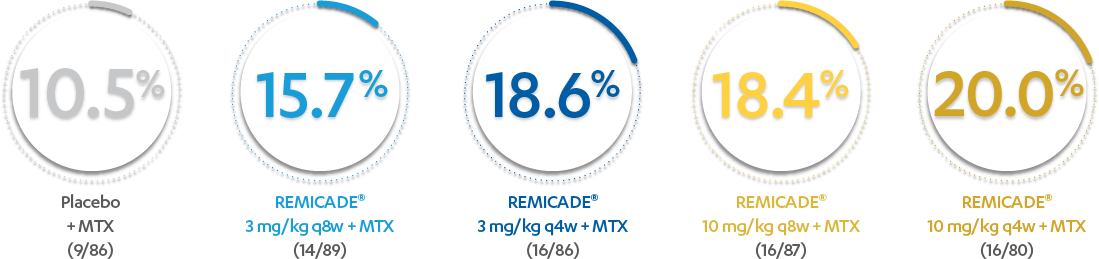
ACR20 RESPONSE RATES IN ADULTS WITH MODERATELY TO SEVERELY ACTIVE RA AT WEEK 30:

In the evaluation of ACR20 data, patients who discontinued treatment through Week 54 were considered to be ACR nonresponders.
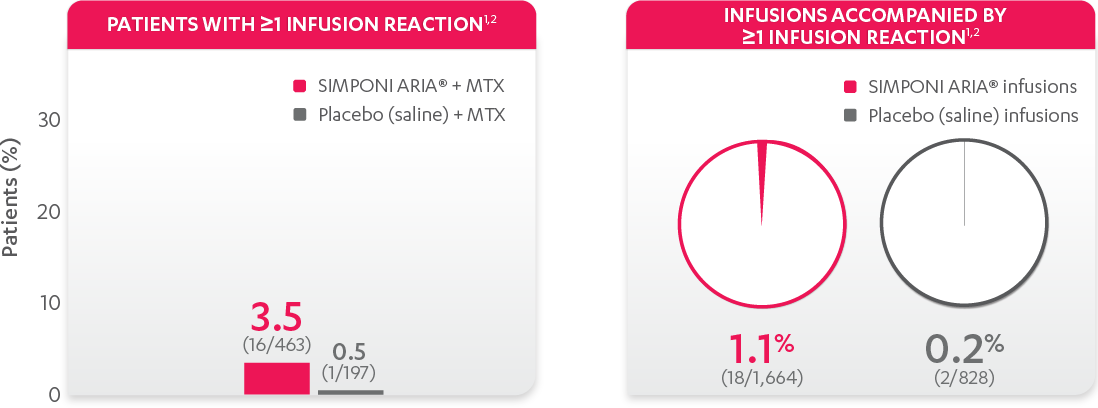
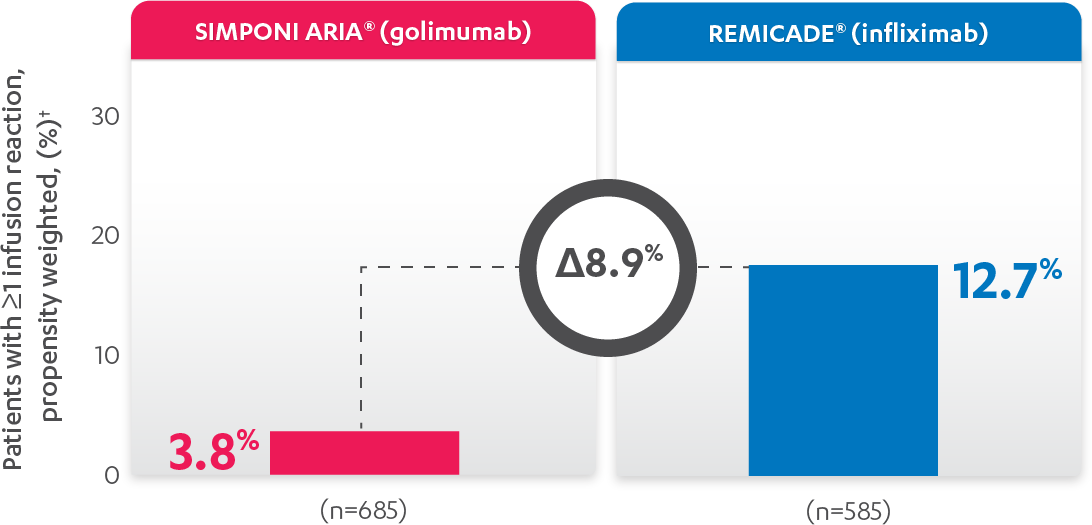
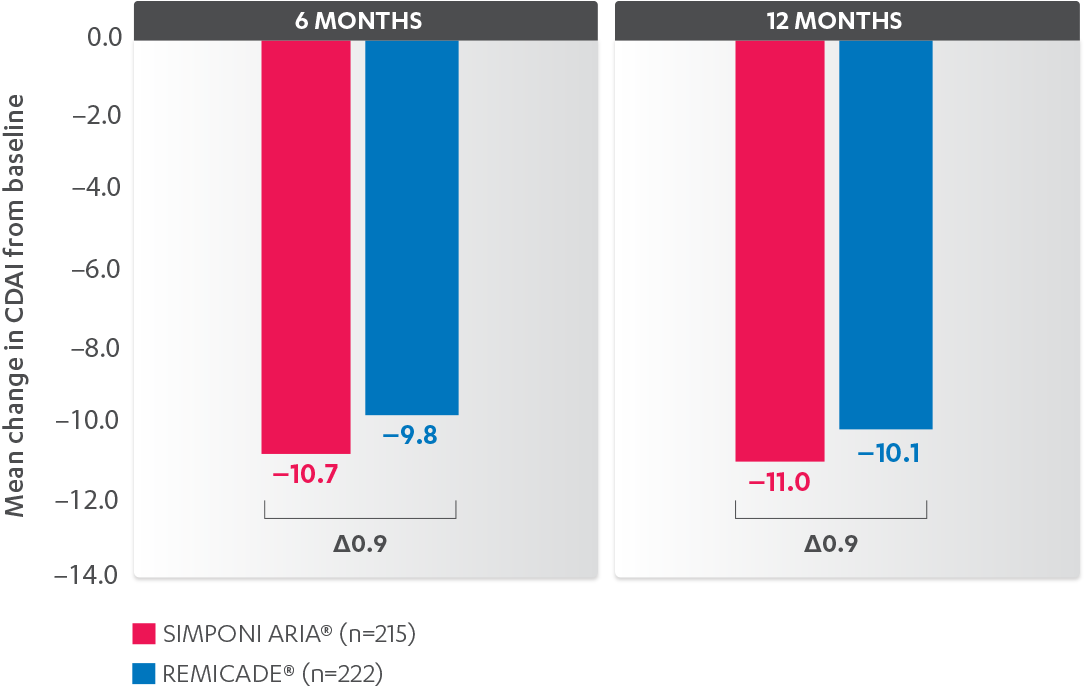
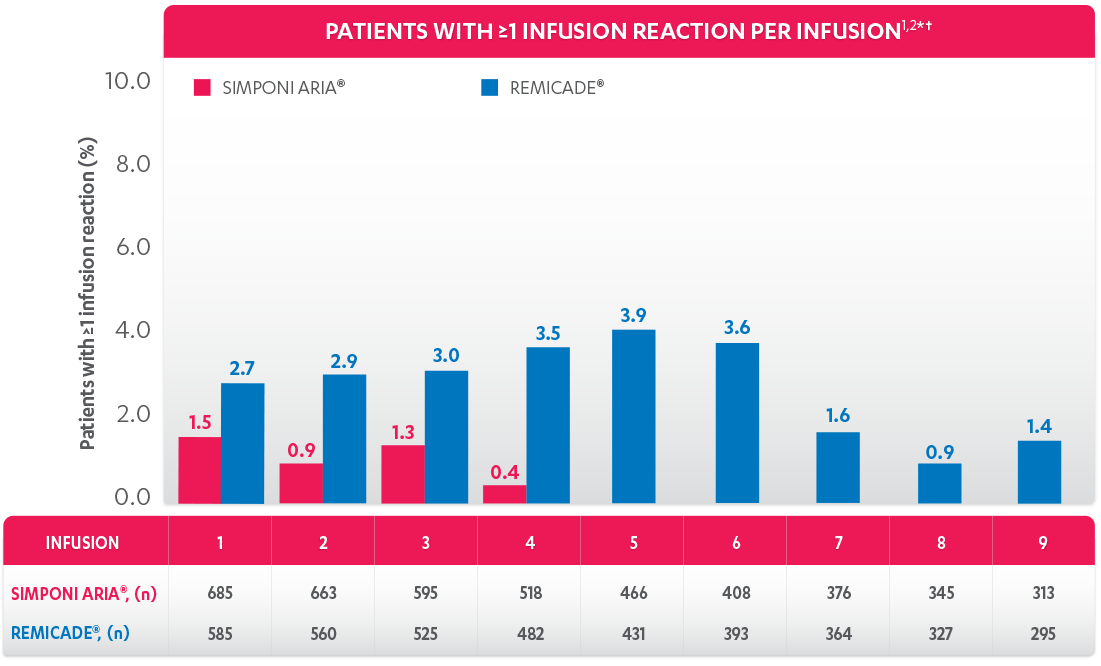
DEMONSTRATED SAFETY PROFILE THROUGH WEEK 302,3

PATIENTS (%) WITH ≥1 INFUSION REACTION THROUGH WEEK 303*
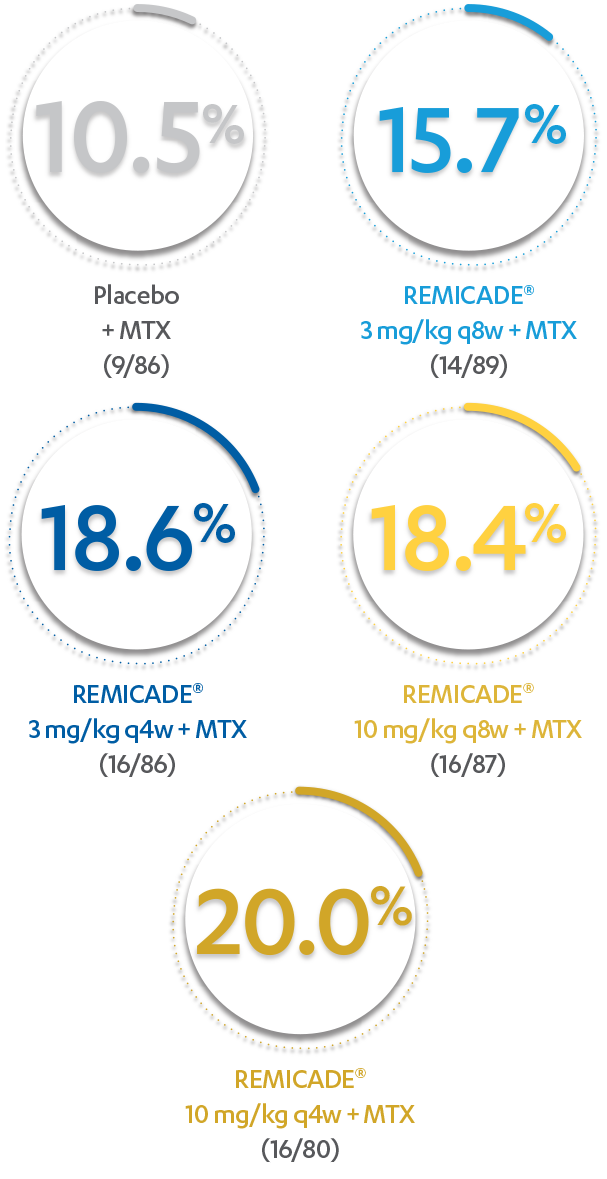
*Infusion reaction: Any AE occurring during an infusion or within 1 hour following completion of the infusion.
ATTRACT
REMICADE®
- REMICADE®, in combination with MTX, is indicated for reducing the signs and symptoms, inhibiting the progression of structural damage, and improving physical function in patients with moderately to severely active RA
- The recommended dose of REMICADE® is 3 mg/kg given as an intravenous induction regimen at 0, 2, and 6 weeks, followed by a maintenance regimen of 3 mg/kg every 8 weeks thereafter for the treatment of moderately to severely active RA1
- REMICADE® should be given in combination with MTX1
- For patients who have an incomplete response, consideration may be given to adjusting the dose up to 10 mg/kg or treating as often as every 4 weeks, bearing in mind that risk of serious infections is increased at higher doses1

IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
SERIOUS INFECTIONS
Patients treated with REMICADE® (infliximab) are at increased risk for developing serious infections that may lead to hospitalization or death. Most patients who developed these infections were taking concomitant immunosuppressants such as methotrexate or corticosteroids. Discontinue REMICADE® if a patient develops a serious infection or sepsis.
Reported infections include:
- Active tuberculosis (TB), including reactivation of latent TB. Patients frequently presented with disseminated or extrapulmonary disease. Patients should be tested for latent TB before and during treatment with REMICADE®.1,2 Treatment for latent infection should be initiated prior to treatment with REMICADE®.
- Invasive fungal infections, including histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, candidiasis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, pneumocystosis, and cryptococcosis. Patients may present with disseminated, rather than localized, disease. Empiric anti-fungal therapy should be considered in patients at risk for invasive fungal infections who develop severe systemic illness.
- Bacterial, viral, and other infections due to opportunistic pathogens, including Legionella, Listeria, and Salmonella.
The risks and benefits of treatment with REMICADE® should be carefully considered prior to initiating therapy in patients with chronic or recurrent infection. Closely monitor patients for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment with REMICADE®, including the possible development of TB in patients who tested negative for latent TB infection prior to initiating therapy, who are on treatment for latent TB, or who were previously treated for TB infection.
Risk of infection may be higher in patients greater than 65 years of age, pediatric patients, patients with co-morbid conditions and/or patients taking concomitant immunosuppressant therapy. In clinical trials, other serious infections observed in patients treated with REMICADE® included pneumonia, cellulitis, abscess, and skin ulceration.
MALIGNANCIES
cp-62063v2Lymphoma and other malignancies, some fatal, have been reported in children and adolescent patients treated with TNF blockers, including REMICADE®. Approximately half of these cases were lymphomas, including Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. The other cases represented a variety of malignancies, including rare malignancies that are usually associated with immunosuppression and malignancies that are not usually observed in children and adolescents. The malignancies occurred after a median of 30 months after the first dose of therapy. Most of the patients were receiving concomitant immunosuppressants.
Postmarketing cases of hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma, a rare type of T-cell lymphoma, have been reported in patients treated with TNF blockers, including REMICADE®. These cases have had a very aggressive disease course and have been fatal. The majority of reported REMICADE® cases have occurred in patients with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis and most were in adolescent and young adult males. Almost all of these patients had received treatment with azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine concomitantly with REMICADE® at or prior to diagnosis. Carefully assess the risks and benefits of treatment with REMICADE®, especially in these patient types.
In clinical trials of all TNF blockers, more cases of lymphoma were observed compared with controls and the expected rate in the general population. However, patients with Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, or plaque psoriasis may be at higher risk for developing lymphoma. In clinical trials of some TNF blockers, including REMICADE®, more cases of other malignancies were observed compared with controls. The rate of these malignancies among patients treated with REMICADE® was similar to that expected in the general population whereas the rate in control patients was lower than expected. Cases of acute and chronic leukemia have been reported with postmarketing TNF-blocker use. As the potential role of TNF blockers in the development of malignancies is not known, caution should be exercised when considering treatment of patients with a current or a past history of malignancy or other risk factors such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Melanoma and Merkel cell carcinoma have been reported in patients treated with TNF‑blocker therapy, including REMICADE®. Periodic skin examination is recommended for all patients, particularly those with risk factors for skin cancer.
A population-based retrospective cohort study found a 2- to 3-fold increase in the incidence of invasive cervical cancer in women with rheumatoid arthritis treated with REMICADE® compared to biologics-naïve patients or the general population, particularly those over 60 years of age. A causal relationship between REMICADE® and cervical cancer cannot be excluded. Periodic screening should continue in women treated with REMICADE®.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
The use of REMICADE® at doses >5 mg/kg is contraindicated in patients with moderate or severe heart failure. REMICADE® is contraindicated in patients with a previous severe hypersensitivity reaction to infliximab or any of the inactive ingredients of REMICADE® or any murine proteins (severe hypersensitivity reactions have included anaphylaxis, hypotension, and serum sickness).
HEPATITIS B REACTIVATION
TNF blockers, including REMICADE®, have been associated with reactivation of hepatitis B virus (HBV) in patients who are chronic carriers. Some cases were fatal. Patients should be tested for HBV infection before initiating REMICADE®. For patients who test positive, consult a physician with expertise in the treatment of hepatitis B. Exercise caution when prescribing REMICADE® for patients identified as carriers of HBV and monitor closely for active HBV infection during and following termination of therapy with REMICADE®. Discontinue REMICADE® in patients who develop HBV reactivation and initiate antiviral therapy with appropriate supportive treatment. Exercise caution when considering resumption of REMICADE® and monitor patients closely.
HEPATOTOXICITY
Severe hepatic reactions, including acute liver failure, jaundice, hepatitis, and cholestasis have been reported in patients receiving REMICADE® postmarketing. Some cases were fatal or required liver transplant. Aminotransferase elevations were not noted prior to discovery of liver injury in many cases. Patients with symptoms or signs of liver dysfunction should be evaluated for evidence of liver injury. If jaundice and/or marked liver enzyme elevations (eg, ≥5 times the upper limit of normal) develop, REMICADE® should be discontinued, and a thorough investigation of the abnormality should be undertaken.
HEART FAILURE
In a randomized, placebo-controlled study in patients with moderate or severe heart failure (NYHA Functional Class III/IV), higher mortality rates and a higher risk of hospitalization were observed at Week 28 at a dose of 10 mg/kg and higher rates of cardiovascular events were observed at both 5 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg. There have been postmarketing reports of new onset and worsening heart failure, with and without identifiable precipitating factors. Patients with moderate or severe heart failure taking REMICADE® (≤5 mg/kg) or patients with mild heart failure should be closely monitored and treatment should be discontinued if new or worsening symptoms appear.
HEMATOLOGIC EVENTS
Cases of leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and pancytopenia (some fatal) have been reported. The causal relationship to REMICADE® therapy remains unclear. Exercise caution in patients who have ongoing or a history of significant hematologic abnormalities. Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if they develop signs and symptoms of blood dyscrasias or infection. Consider discontinuation of REMICADE® in patients who develop significant hematologic abnormalities.
HYPERSENSITIVITY
REMICADE® has been associated with hypersensitivity reactions that differ in their time of onset. Anaphylaxis, acute urticaria, dyspnea, and hypotension have occurred in association with infusions of REMICADE®. Medications for the treatment of hypersensitivity reactions should be available.
CARDIOVASCULAR AND CEREBROVASCULAR REACTIONS DURING AND AFTER INFUSION
Serious cerebrovascular accidents, myocardial ischemia/infarction (some fatal), hypotension, hypertension, and arrhythmias have been reported during and within 24 hours of initiation of REMICADE® infusion. Cases of transient visual loss have been reported during or within 2 hours of REMICADE® infusion. Monitor patients during infusion and if a serious reaction occurs, discontinue infusion. Manage reactions according to signs and symptoms.
NEUROLOGIC EVENTS
TNF blockers, including REMICADE®, have been associated with CNS manifestation of systemic vasculitis, seizure, and new onset or exacerbation of CNS demyelinating disorders, including multiple sclerosis and optic neuritis, and peripheral demyelinating disorders, including Guillain- Barré syndrome. Exercise caution when considering REMICADE® in patients with these disorders and consider discontinuation if these disorders develop.
CONCURRENT ADMINISTRATION WITH OTHER BIOLOGICS
Concurrent use of REMICADE® with anakinra, abatacept, tocilizumab, or other biologics used to treat the same conditions as REMICADE® is not recommended because of the possibility of an increased risk of infection. Care should be taken when switching from one biologic to another, since overlapping biological activity may further increase the risk of infection.
AUTOIMMUNITY
Treatment with REMICADE® may result in the formation of autoantibodies and in the development of a lupus-like syndrome. Discontinue treatment if symptoms of a lupus-like syndrome develop.
VACCINATIONS AND USE OF LIVE VACCINES/THERAPEUTIC INFECTIOUS AGENTS
Prior to initiating REMICADE®, update vaccinations in accordance with current vaccination guidelines. Live vaccines or therapeutic infectious agents should not be given with REMICADE® due to the possibility of clinical infections, including disseminated infections.
At least a 6-month waiting period following birth is recommended before the administration of any live vaccine to infants exposed in utero to REMICADE®.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In clinical trials, the most common adverse reactions occurring in >10% of REMICADE®-treated patients included infections (eg, upper respiratory, sinusitis, and pharyngitis), infusion-related reactions, headache, and abdominal pain.
For more information, please see the full Prescribing Information and Medication Guide for REMICADE®. Provide the Medication Guide to your patients and encourage discussion.
Indication for
REMICADE® (infliximab)
INDICATION
REMICADE®, in combination with methotrexate, is indicated for reducing signs and symptoms, inhibiting the progression of structural damage, and improving physical function in adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
SERIOUS INFECTIONS
Patients treated with SIMPONI ARIA® (golimumab) are at increased risk for developing serious infections that may lead to hospitalization or death. Most patients who developed these infections were taking concomitant immunosuppressants such as methotrexate or corticosteroids. Discontinue SIMPONI ARIA® if a patient develops a serious infection.
Reported infections with TNF blockers, of which SIMPONI ARIA® is a member, include:
- Active tuberculosis (TB), including reactivation of latent TB. Patients frequently presented with disseminated or extrapulmonary disease. Test patients for latent TB before SIMPONI ARIA® use and during therapy. Initiate treatment for latent infection prior to SIMPONI ARIA® use.
- Invasive fungal infections, including histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, candidiasis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, and pneumocystosis. Patients with histoplasmosis or other invasive fungal infections may present with disseminated, rather than localized, disease. Consider empiric anti-fungal therapy in patients at risk for invasive fungal infections who develop severe systemic illness.
- Bacterial, viral, and other infections due to opportunistic pathogens, including Legionella and Listeria.
Consider the risks and benefits of treatment with SIMPONI ARIA® prior to initiating therapy in patients with chronic or recurrent infection. Do not start SIMPONI ARIA® in patients with clinically important active infections, including localized infections. Closely monitor patients for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment with SIMPONI ARIA®, including the possible development of TB in patients who tested negative for latent TB infection prior to initiating therapy, who are on treatment for latent TB, or who were previously treated for TB infection.
Risk of infection may be higher in patients greater than 65 years of age, patients with co-morbid conditions and/or patients taking concomitant immunosuppressant therapy. Other serious infections observed in patients treated with SIMPONI ARIA® included sepsis, pneumonia, cellulitis, and abscess.
MALIGNANCIES
cp-51207v3Malignancies, some fatal, have been reported in children, adolescents, and young adult patients treated with golimumab. Approximately half the cases were lymphomas, including Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. The other cases represented a variety of malignancies, including rare malignancies usually associated with immunosuppression and malignancies not usually observed in children or adolescents. Malignancies occurred after a median of 30 months after the first dose of therapy. Most of the patients were receiving concomitant immunosuppressants.
In the controlled portions of clinical trials of TNF blockers including the subcutaneous formulation of golimumab, more cases of lymphoma have been observed among patients receiving anti-TNF treatment compared with patients in the control groups. In clinical trials, the incidence of malignancies other than lymphoma and non-melanoma skin cancer per 100 patient-years of follow-up was 0.56 (95% CI: 0.01, 3.11) in the SIMPONI ARIA® group compared with an incidence of 0 (95% CI: 0.00, 3.79) in the placebo group. Cases of acute and chronic leukemia have been reported with TNF-blocker use, including SIMPONI ARIA®. The risks and benefits of TNF-blocker therapy should be considered prior to initiating therapy in patients with a known malignancy or who develop a malignancy.
Postmarketing cases of hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma (HSTCL), a rare type of T-cell lymphoma, have been reported in patients treated with TNF blockers. These cases have had a very aggressive disease course and have been fatal. Nearly all reported cases have occurred in patients with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, and the majority were in adolescent and young adult males. Almost all of these patients had received treatment with azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine concomitantly with a TNF blocker at or prior to diagnosis. A risk for the development for HSTCL in patients treated with TNF blockers cannot be excluded.
Melanoma and Merkel cell carcinoma have been reported in patients treated with TNF-blocking agents, including SIMPONI ARIA®. Periodic skin examination is recommended for all patients, particularly those with risk factors for skin cancer.
HEPATITIS B REACTIVATION
The use of TNF blockers, of which SIMPONI ARIA® is a member, has been associated with reactivation of hepatitis B virus (HBV) in patients who are chronic hepatitis B carriers. In some instances, HBV reactivation occurring in conjunction with TNF-blocker therapy has been fatal. The majority of these reports have occurred in patients who received concomitant immunosuppressants.
All patients should be tested for HBV infection before initiating TNF-blocker therapy. For patients who test positive for hepatitis B surface antigen, consult a physician with expertise in the treatment of hepatitis B before initiating TNF-blocker therapy. Exercise caution when prescribing SIMPONI ARIA® for patients identified as carriers of HBV and closely monitor for active HBV infection during and following termination of therapy with SIMPONI ARIA®. Discontinue SIMPONI ARIA® in patients who develop HBV reactivation, and initiate antiviral therapy with appropriate supportive treatment. Exercise caution when considering resumption of SIMPONI ARIA®, and monitor patients closely.
CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE
Cases of worsening congestive heart failure (CHF) and new-onset CHF have been reported with TNF blockers, including SIMPONI ARIA®. Some cases had a fatal outcome. Exercise caution in CHF patients receiving SIMPONI ARIA® and monitor them closely during therapy. Discontinue SIMPONI ARIA® if new or worsening symptoms of heart failure appear.
DEMYELINATING DISORDERS
Use of TNF blockers, including SIMPONI ARIA®, has been associated with rare cases of new-onset or exacerbation of demyelinating disorders, including multiple sclerosis (MS) and Guillain-Barré syndrome. Cases of central demyelination, MS, optic neuritis, and peripheral demyelinating polyneuropathy have rarely been reported in patients treated with golimumab. Exercise caution in considering the use of SIMPONI ARIA® in patients with these disorders. Consider discontinuation if these disorders develop.
AUTOIMMUNITY
Treatment with TNF blockers, including SIMPONI ARIA®, may result in the formation of antinuclear antibodies. Rarely, treatment with TNF blockers may result in a lupus-like syndrome. Discontinue treatment if symptoms of a lupus-like syndrome develop.
USE WITH OTHER DRUGS
The concomitant use of a TNF blocker and abatacept or anakinra was associated with a higher risk of serious infections, therefore the use of SIMPONI ARIA® in combination with these products is not recommended. Care should be taken when switching from one biologic to another since overlapping biological activity may further increase the risk of infection. A higher rate of serious infections has also been observed in RA patients treated with rituximab who received subsequent treatment with a TNF blocker. The concomitant use of SIMPONI ARIA® with biologics approved to treat RA is not recommended because of the possibility of an increased risk of infection.
HEMATOLOGIC CYTOPENIAS
There have been reports of pancytopenia, leukopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, and thrombocytopenia in patients receiving SIMPONI ARIA®. Exercise caution when using SIMPONI ARIA® in patients who have or had significant cytopenias.
VACCINATIONS/THERAPEUTIC INFECTIOUS AGENTS
Live vaccines or therapeutic infectious agents should not be given with SIMPONI ARIA® due to the possibility of clinical infections, including disseminated infections.
Update vaccinations prior to initiation of treatment in accordance with current vaccination guidelines. Advise patients to discuss with the physician before seeking any immunizations. At least a 6-month waiting period following birth is recommended before the administration of any live vaccine to infants exposed in utero to SIMPONI ARIA®.
HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS
Serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylaxis) have been reported following administration of the subcutaneous formulation of golimumab and SIMPONI ARIA®, some occurring after the first dose. Hypersensitivity reactions including hives, pruritus, dyspnea, and nausea, were reported in association with infusions of SIMPONI ARIA®. If an anaphylactic or other serious allergic reaction occurs, discontinue SIMPONI ARIA® immediately and institute appropriate therapy.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most serious adverse reactions were serious infections and malignancies.
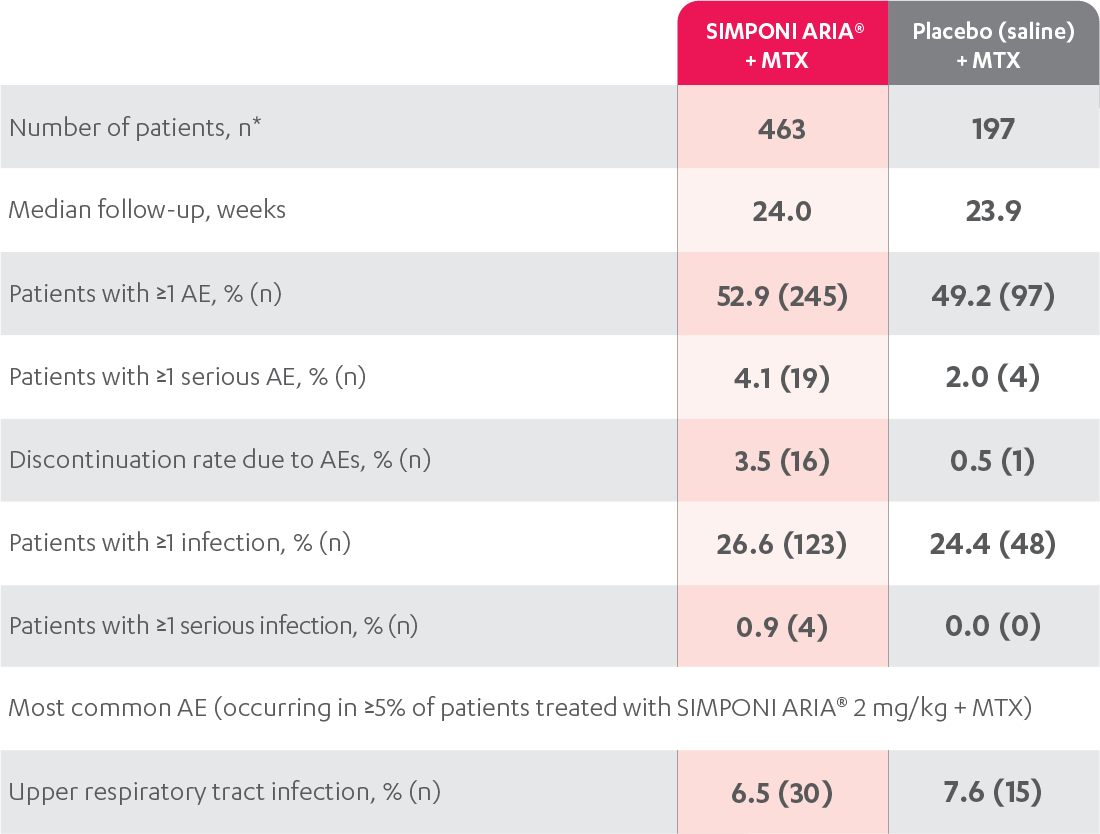
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥3%) reported in clinical trials were: upper respiratory tract infection, alanine aminotransferase increase, viral infection, aspartate aminotransferase increase, neutrophil count decrease, bronchitis, hypertension, and rash. In the controlled phase of Trial RA, the rate of infusions associated with an infusion reaction was reported in 1.1% of SIMPONI ARIA® infusions compared with 0.2% of infusions in the control group.
The adverse reactions observed in pediatric patients with polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (pJIA) were consistent with the established safety profile of SIMPONI ARIA® in adult patients with RA and PsA.
Please see the full Prescribing Information and Medication Guide for SIMPONI ARIA®. Provide the Medication Guide to your patients and encourage discussion.
Indication for
SIMPONI ARIA® (golimumab)
INDICATION
SIMPONI ARIA® is indicated for the treatment of adults with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in combination with methotrexate (MTX).
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
SERIOUS INFECTIONS
Patients treated with SIMPONI ARIA® (golimumab) are at increased risk for developing serious infections that may lead to hospitalization or death. Most patients who developed these infections were taking concomitant immunosuppressants such as methotrexate or corticosteroids. Discontinue SIMPONI ARIA® if a patient develops a serious infection.
Reported infections with TNF blockers, of which SIMPONI ARIA® is a member, include:
- Active tuberculosis (TB), including reactivation of latent TB. Patients frequently presented with disseminated or extrapulmonary disease. Test patients for latent TB before SIMPONI ARIA® use and during therapy. Initiate treatment for latent infection prior to SIMPONI ARIA® use.
- Invasive fungal infections, including histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, candidiasis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, and pneumocystosis. Patients with histoplasmosis or other invasive fungal infections may present with disseminated, rather than localized, disease. Consider empiric anti-fungal therapy in patients at risk for invasive fungal infections who develop severe systemic illness.
- Bacterial, viral, and other infections due to opportunistic pathogens, including Legionella and Listeria.
Consider the risks and benefits of treatment with SIMPONI ARIA® prior to initiating therapy in patients with chronic or recurrent infection. Do not start SIMPONI ARIA® in patients with clinically important active infections, including localized infections. Closely monitor patients for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment with SIMPONI ARIA®, including the possible development of TB in patients who tested negative for latent TB infection prior to initiating therapy, who are on treatment for latent TB, or who were previously treated for TB infection.
Risk of infection may be higher in patients greater than 65 years of age, patients with co-morbid conditions and/or patients taking concomitant immunosuppressant therapy. Other serious infections observed in patients treated with SIMPONI ARIA® included sepsis, pneumonia, cellulitis, and abscess.
MALIGNANCIES
cp-51207v3Malignancies, some fatal, have been reported in children, adolescents, and young adult patients treated with golimumab. Approximately half the cases were lymphomas, including Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. The other cases represented a variety of malignancies, including rare malignancies usually associated with immunosuppression and malignancies not usually observed in children or adolescents. Malignancies occurred after a median of 30 months after the first dose of therapy. Most of the patients were receiving concomitant immunosuppressants.
In the controlled portions of clinical trials of TNF blockers including the subcutaneous formulation of golimumab, more cases of lymphoma have been observed among patients receiving anti-TNF treatment compared with patients in the control groups. In clinical trials, the incidence of malignancies other than lymphoma and non-melanoma skin cancer per 100 patient-years of follow-up was 0.56 (95% CI: 0.01, 3.11) in the SIMPONI ARIA® group compared with an incidence of 0 (95% CI: 0.00, 3.79) in the placebo group. Cases of acute and chronic leukemia have been reported with TNF-blocker use, including SIMPONI ARIA®. The risks and benefits of TNF-blocker therapy should be considered prior to initiating therapy in patients with a known malignancy or who develop a malignancy.
Postmarketing cases of hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma (HSTCL), a rare type of T-cell lymphoma, have been reported in patients treated with TNF blockers. These cases have had a very aggressive disease course and have been fatal. Nearly all reported cases have occurred in patients with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, and the majority were in adolescent and young adult males. Almost all of these patients had received treatment with azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine concomitantly with a TNF blocker at or prior to diagnosis. A risk for the development for HSTCL in patients treated with TNF blockers cannot be excluded.
Melanoma and Merkel cell carcinoma have been reported in patients treated with TNF-blocking agents, including SIMPONI ARIA®. Periodic skin examination is recommended for all patients, particularly those with risk factors for skin cancer.
HEPATITIS B REACTIVATION
The use of TNF blockers, of which SIMPONI ARIA® is a member, has been associated with reactivation of hepatitis B virus (HBV) in patients who are chronic hepatitis B carriers. In some instances, HBV reactivation occurring in conjunction with TNF-blocker therapy has been fatal. The majority of these reports have occurred in patients who received concomitant immunosuppressants.
All patients should be tested for HBV infection before initiating TNF-blocker therapy. For patients who test positive for hepatitis B surface antigen, consult a physician with expertise in the treatment of hepatitis B before initiating TNF-blocker therapy. Exercise caution when prescribing SIMPONI ARIA® for patients identified as carriers of HBV and closely monitor for active HBV infection during and following termination of therapy with SIMPONI ARIA®. Discontinue SIMPONI ARIA® in patients who develop HBV reactivation, and initiate antiviral therapy with appropriate supportive treatment. Exercise caution when considering resumption of SIMPONI ARIA®, and monitor patients closely.
CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE
Cases of worsening congestive heart failure (CHF) and new-onset CHF have been reported with TNF blockers, including SIMPONI ARIA®. Some cases had a fatal outcome. Exercise caution in CHF patients receiving SIMPONI ARIA® and monitor them closely during therapy. Discontinue SIMPONI ARIA® if new or worsening symptoms of heart failure appear.
DEMYELINATING DISORDERS
Use of TNF blockers, including SIMPONI ARIA®, has been associated with rare cases of new-onset or exacerbation of demyelinating disorders, including multiple sclerosis (MS) and Guillain-Barré syndrome. Cases of central demyelination, MS, optic neuritis, and peripheral demyelinating polyneuropathy have rarely been reported in patients treated with golimumab. Exercise caution in considering the use of SIMPONI ARIA® in patients with these disorders. Consider discontinuation if these disorders develop.
AUTOIMMUNITY
Treatment with TNF blockers, including SIMPONI ARIA®, may result in the formation of antinuclear antibodies. Rarely, treatment with TNF blockers may result in a lupus-like syndrome. Discontinue treatment if symptoms of a lupus-like syndrome develop.
USE WITH OTHER DRUGS
The concomitant use of a TNF blocker and abatacept or anakinra was associated with a higher risk of serious infections, therefore the use of SIMPONI ARIA® in combination with these products is not recommended. Care should be taken when switching from one biologic to another since overlapping biological activity may further increase the risk of infection. A higher rate of serious infections has also been observed in RA patients treated with rituximab who received subsequent treatment with a TNF blocker. The concomitant use of SIMPONI ARIA® with biologics approved to treat RA is not recommended because of the possibility of an increased risk of infection.
HEMATOLOGIC CYTOPENIAS
There have been reports of pancytopenia, leukopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, and thrombocytopenia in patients receiving SIMPONI ARIA®. Exercise caution when using SIMPONI ARIA® in patients who have or had significant cytopenias.
VACCINATIONS/THERAPEUTIC INFECTIOUS AGENTS
Live vaccines or therapeutic infectious agents should not be given with SIMPONI ARIA® due to the possibility of clinical infections, including disseminated infections.
Update vaccinations prior to initiation of treatment in accordance with current vaccination guidelines. Advise patients to discuss with the physician before seeking any immunizations. At least a 6-month waiting period following birth is recommended before the administration of any live vaccine to infants exposed in utero to SIMPONI ARIA®.
HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS
Serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylaxis) have been reported following administration of the subcutaneous formulation of golimumab and SIMPONI ARIA®, some occurring after the first dose. Hypersensitivity reactions including hives, pruritus, dyspnea, and nausea, were reported in association with infusions of SIMPONI ARIA®. If an anaphylactic or other serious allergic reaction occurs, discontinue SIMPONI ARIA® immediately and institute appropriate therapy.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most serious adverse reactions were serious infections and malignancies.
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥3%) reported in clinical trials were: upper respiratory tract infection, alanine aminotransferase increase, viral infection, aspartate aminotransferase increase, neutrophil count decrease, bronchitis, hypertension, and rash. In the controlled phase of Trial RA, the rate of infusions associated with an infusion reaction was reported in 1.1% of SIMPONI ARIA® infusions compared with 0.2% of infusions in the control group.
The adverse reactions observed in pediatric patients with polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (pJIA) were consistent with the established safety profile of SIMPONI ARIA® in adult patients with RA and PsA.
Please see the full Prescribing Information and Medication Guide for SIMPONI ARIA®. Provide the Medication Guide to your patients and encourage discussion.
Indication for
SIMPONI ARIA® (golimumab)
INDICATION
SIMPONI ARIA® is indicated for the treatment of adults with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in combination with methotrexate (MTX).
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
SERIOUS INFECTIONS
Patients treated with REMICADE® (infliximab) are at increased risk for developing serious infections that may lead to hospitalization or death. Most patients who developed these infections were taking concomitant immunosuppressants such as methotrexate or corticosteroids. Discontinue REMICADE® if a patient develops a serious infection or sepsis.
Reported infections include:
- Active tuberculosis (TB), including reactivation of latent TB. Patients frequently presented with disseminated or extrapulmonary disease. Patients should be tested for latent TB before and during treatment with REMICADE®.1,2 Treatment for latent infection should be initiated prior to treatment with REMICADE®.
- Invasive fungal infections, including histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, candidiasis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, pneumocystosis, and cryptococcosis. Patients may present with disseminated, rather than localized, disease. Empiric anti-fungal therapy should be considered in patients at risk for invasive fungal infections who develop severe systemic illness.
- Bacterial, viral, and other infections due to opportunistic pathogens, including Legionella, Listeria, and Salmonella.
The risks and benefits of treatment with REMICADE® should be carefully considered prior to initiating therapy in patients with chronic or recurrent infection. Closely monitor patients for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment with REMICADE®, including the possible development of TB in patients who tested negative for latent TB infection prior to initiating therapy, who are on treatment for latent TB, or who were previously treated for TB infection.
Risk of infection may be higher in patients greater than 65 years of age, pediatric patients, patients with co-morbid conditions and/or patients taking concomitant immunosuppressant therapy. In clinical trials, other serious infections observed in patients treated with REMICADE® included pneumonia, cellulitis, abscess, and skin ulceration.
MALIGNANCIES
cp-62063v2Lymphoma and other malignancies, some fatal, have been reported in children and adolescent patients treated with TNF blockers, including REMICADE®. Approximately half of these cases were lymphomas, including Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. The other cases represented a variety of malignancies, including rare malignancies that are usually associated with immunosuppression and malignancies that are not usually observed in children and adolescents. The malignancies occurred after a median of 30 months after the first dose of therapy. Most of the patients were receiving concomitant immunosuppressants.
Postmarketing cases of hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma, a rare type of T-cell lymphoma, have been reported in patients treated with TNF blockers, including REMICADE®. These cases have had a very aggressive disease course and have been fatal. The majority of reported REMICADE® cases have occurred in patients with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis and most were in adolescent and young adult males. Almost all of these patients had received treatment with azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine concomitantly with REMICADE® at or prior to diagnosis. Carefully assess the risks and benefits of treatment with REMICADE®, especially in these patient types.
In clinical trials of all TNF blockers, more cases of lymphoma were observed compared with controls and the expected rate in the general population. However, patients with Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, or plaque psoriasis may be at higher risk for developing lymphoma. In clinical trials of some TNF blockers, including REMICADE®, more cases of other malignancies were observed compared with controls. The rate of these malignancies among patients treated with REMICADE® was similar to that expected in the general population whereas the rate in control patients was lower than expected. Cases of acute and chronic leukemia have been reported with postmarketing TNF-blocker use. As the potential role of TNF blockers in the development of malignancies is not known, caution should be exercised when considering treatment of patients with a current or a past history of malignancy or other risk factors such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Melanoma and Merkel cell carcinoma have been reported in patients treated with TNF‑blocker therapy, including REMICADE®. Periodic skin examination is recommended for all patients, particularly those with risk factors for skin cancer.
A population-based retrospective cohort study found a 2- to 3-fold increase in the incidence of invasive cervical cancer in women with rheumatoid arthritis treated with REMICADE® compared to biologics-naïve patients or the general population, particularly those over 60 years of age. A causal relationship between REMICADE® and cervical cancer cannot be excluded. Periodic screening should continue in women treated with REMICADE®.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
The use of REMICADE® at doses >5 mg/kg is contraindicated in patients with moderate or severe heart failure. REMICADE® is contraindicated in patients with a previous severe hypersensitivity reaction to infliximab or any of the inactive ingredients of REMICADE® or any murine proteins (severe hypersensitivity reactions have included anaphylaxis, hypotension, and serum sickness).
HEPATITIS B REACTIVATION
TNF blockers, including REMICADE®, have been associated with reactivation of hepatitis B virus (HBV) in patients who are chronic carriers. Some cases were fatal. Patients should be tested for HBV infection before initiating REMICADE®. For patients who test positive, consult a physician with expertise in the treatment of hepatitis B. Exercise caution when prescribing REMICADE® for patients identified as carriers of HBV and monitor closely for active HBV infection during and following termination of therapy with REMICADE®. Discontinue REMICADE® in patients who develop HBV reactivation and initiate antiviral therapy with appropriate supportive treatment. Exercise caution when considering resumption of REMICADE® and monitor patients closely.
HEPATOTOXICITY
Severe hepatic reactions, including acute liver failure, jaundice, hepatitis, and cholestasis have been reported in patients receiving REMICADE® postmarketing. Some cases were fatal or required liver transplant. Aminotransferase elevations were not noted prior to discovery of liver injury in many cases. Patients with symptoms or signs of liver dysfunction should be evaluated for evidence of liver injury. If jaundice and/or marked liver enzyme elevations (eg, ≥5 times the upper limit of normal) develop, REMICADE® should be discontinued, and a thorough investigation of the abnormality should be undertaken.
HEART FAILURE
In a randomized, placebo-controlled study in patients with moderate or severe heart failure (NYHA Functional Class III/IV), higher mortality rates and a higher risk of hospitalization were observed at Week 28 at a dose of 10 mg/kg and higher rates of cardiovascular events were observed at both 5 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg. There have been postmarketing reports of new onset and worsening heart failure, with and without identifiable precipitating factors. Patients with moderate or severe heart failure taking REMICADE® (≤5 mg/kg) or patients with mild heart failure should be closely monitored and treatment should be discontinued if new or worsening symptoms appear.
HEMATOLOGIC EVENTS
Cases of leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and pancytopenia (some fatal) have been reported. The causal relationship to REMICADE® therapy remains unclear. Exercise caution in patients who have ongoing or a history of significant hematologic abnormalities. Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if they develop signs and symptoms of blood dyscrasias or infection. Consider discontinuation of REMICADE® in patients who develop significant hematologic abnormalities.
HYPERSENSITIVITY
REMICADE® has been associated with hypersensitivity reactions that differ in their time of onset. Anaphylaxis, acute urticaria, dyspnea, and hypotension have occurred in association with infusions of REMICADE®. Medications for the treatment of hypersensitivity reactions should be available.
CARDIOVASCULAR AND CEREBROVASCULAR REACTIONS DURING AND AFTER INFUSION
Serious cerebrovascular accidents, myocardial ischemia/infarction (some fatal), hypotension, hypertension, and arrhythmias have been reported during and within 24 hours of initiation of REMICADE® infusion. Cases of transient visual loss have been reported during or within 2 hours of REMICADE® infusion. Monitor patients during infusion and if a serious reaction occurs, discontinue infusion. Manage reactions according to signs and symptoms.
NEUROLOGIC EVENTS
TNF blockers, including REMICADE®, have been associated with CNS manifestation of systemic vasculitis, seizure, and new onset or exacerbation of CNS demyelinating disorders, including multiple sclerosis and optic neuritis, and peripheral demyelinating disorders, including Guillain- Barré syndrome. Exercise caution when considering REMICADE® in patients with these disorders and consider discontinuation if these disorders develop.
CONCURRENT ADMINISTRATION WITH OTHER BIOLOGICS
Concurrent use of REMICADE® with anakinra, abatacept, tocilizumab, or other biologics used to treat the same conditions as REMICADE® is not recommended because of the possibility of an increased risk of infection. Care should be taken when switching from one biologic to another, since overlapping biological activity may further increase the risk of infection.
AUTOIMMUNITY
Treatment with REMICADE® may result in the formation of autoantibodies and in the development of a lupus-like syndrome. Discontinue treatment if symptoms of a lupus-like syndrome develop.
VACCINATIONS AND USE OF LIVE VACCINES/THERAPEUTIC INFECTIOUS AGENTS
Prior to initiating REMICADE®, update vaccinations in accordance with current vaccination guidelines. Live vaccines or therapeutic infectious agents should not be given with REMICADE® due to the possibility of clinical infections, including disseminated infections.
At least a 6-month waiting period following birth is recommended before the administration of any live vaccine to infants exposed in utero to REMICADE®.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In clinical trials, the most common adverse reactions occurring in >10% of REMICADE®-treated patients included infections (eg, upper respiratory, sinusitis, and pharyngitis), infusion-related reactions, headache, and abdominal pain.
For more information, please see the full Prescribing Information and Medication Guide for REMICADE®. Provide the Medication Guide to your patients and encourage discussion.
Indication for
REMICADE® (infliximab)
INDICATION
REMICADE®, in combination with methotrexate, is indicated for reducing signs and symptoms, inhibiting the progression of structural damage, and improving physical function in adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA).